Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction: Do Lithium Batteries Really Explode?
Every few months, headlines appear about a phone or an electric scooter catching fire — and people start to wonder: Do lithium batteries really explode?
The truth is, lithium batteries can fail under extreme or improper conditions, but these cases are incredibly rare. Today’s technology — when well designed and correctly used — makes lithium batteries among the safest and most reliable energy sources available.
At Polar ESS, we believe that safety is not just a feature — it’s the foundation of energy innovation. Understanding how lithium batteries work and why failures sometimes occur helps users choose safer products and use them responsibly.
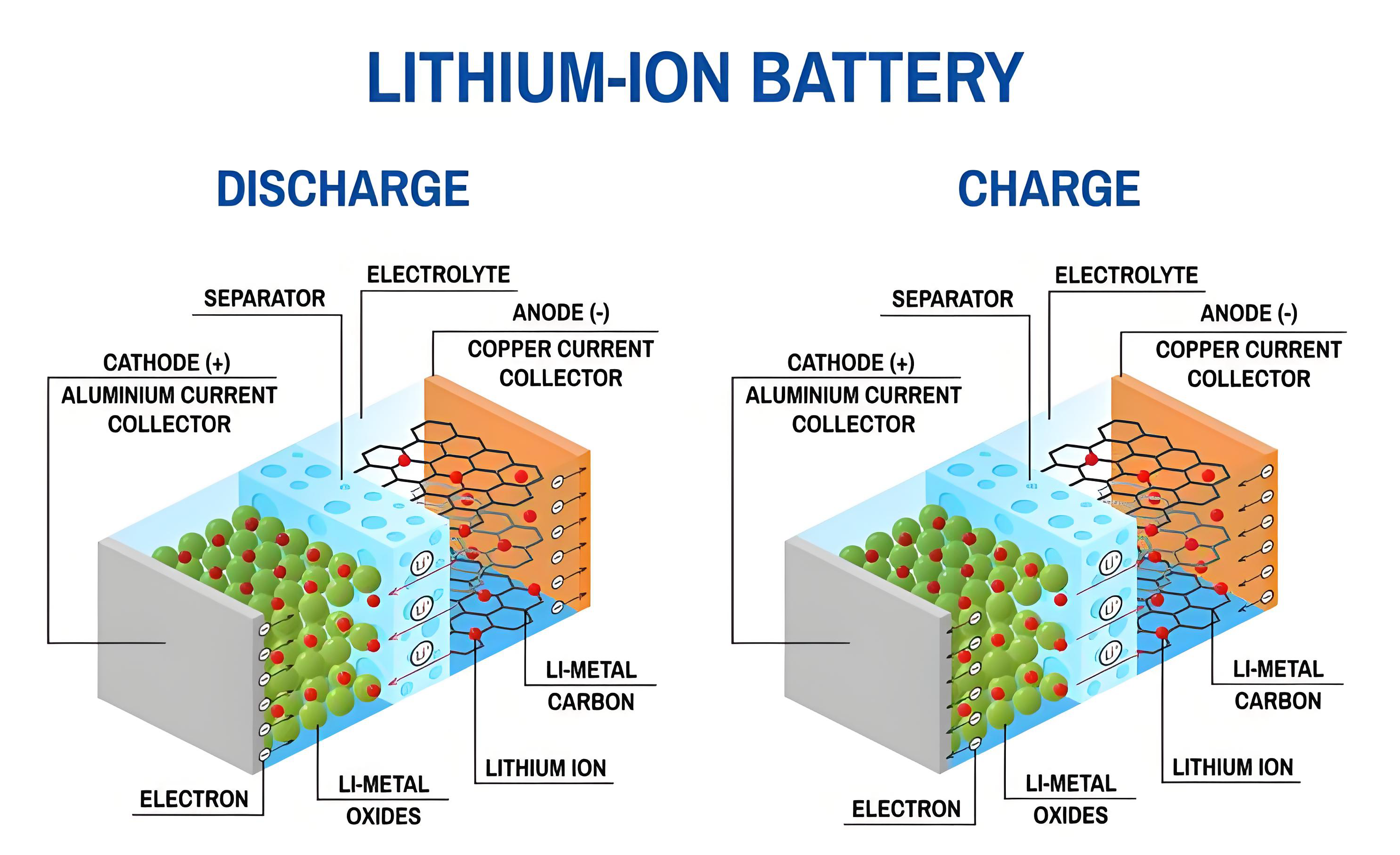
How Do Lithium Batteries Work?
Think of a lithium battery as a busy hive of tiny particles called lithium ions. These ions move back and forth between two electrodes—the positive cathode and the negative anode—through a liquid called electrolyte. When you’re using the battery (discharging), the ions flow from the anode to the cathode, releasing energy. When you charge it, they move back to the anode, storing energy. This efficient process is what powers our modern world, from laptops to home energy storage systems.
However, this high energy density — one of lithium’s greatest strengths — can also be a weakness if not properly managed. If the battery is overcharged, punctured, overheated, or poorly manufactured, internal short circuits or gas buildup may occur, potentially leading to fire or explosion.
That’s why battery management systems (BMS), thermal control, and quality manufacturing are critical for safety.
Why Do Lithium Batteries Explode?
The high energy density that makes lithium batteries so effective also requires careful management. Explosions or fires are typically not spontaneous; they are the result of a process called thermal runaway. This is a chain reaction where the battery overheats, leading to more heat, and eventually to fire or explosion. The main triggers are:
- Physical Damage: Puncturing, Dropping or crushing a battery can create an internal short circuit, instantly generating intense heat.
- Overcharging: Using a faulty or incorrect charger can force too much energy into the battery, damaging its internal structure and leading to overheating.
- Overheating: Exposing a battery to high temperatures (e.g., leaving a phone in a hot car) can push it beyond its safe operating limits.
- Internal Short Circuit: Damaged separators or impurities inside the cells can create a short, generating intense heat.
Poor Quality Manufacturing: Inconsistent materials, lack of protective layers, or low-quality BMS increase the risk significantly.
Fortunately, modern energy storage systems integrate multi-level protection to prevent such conditions long before they become dangerous.
How to Tell If a Lithium Battery Is Unsafe
Your battery often gives you clues before a critical failure. Watch out for these red flags:
- Swelling or Bulging: This is the most common warning sign. Gas builds up inside due to chemical reactions, causing the battery casing to deform. If your device’s case is cracking or the screen is pushing out, stop using it immediately.
- Excessive Heat: A battery that becomes unusually hot during charging or even while idle is a major concern.
- Hissing or Popping Sounds: These noises indicate that the electrolyte is boiling or gas is being released.
- Leaking Fluid: Any sign of leakage is a clear indicator of internal failure.
- Unusual smell or smoke
If you notice any of these signs, stop using the device, move it to a safe, non-flammable area if possible, and consult a professional.
What’s the Explosion Rate of Lithium Batteries?
Despite popular fears, lithium battery explosions are extremely uncommon.
Studies show the failure rate to be approximately 1 in 10 million — meaning you are more likely to be struck by lightning than experience a battery explosion.
What truly determines safety is quality: High-grade materials, strong design standards, and reliable BMS drastically reduce any potential risk.
That’s why choosing a trusted brand with proven safety certifications matters.
Safety by Design: The Polar ESS Approach to Eliminating Risk
We engineer safety into every layer of our systems, turning potential weaknesses into unshakable strengths.
Intelligent, Multi-Layer BMS: Our Battery Management System acts as a vigilant guardian, continuously monitoring voltage, current, and temperature, ready to shut down anomalies in milliseconds.
Thermal Isolation Design: We compartmentalize our battery modules to contain any potential issue and prevent the spread of thermal runaway.
Fire-Retardant Fortification: Our enclosures are built with UL94-V0 rated materials, creating a physical barrier against fire.
Automatic Safety Shutdown: The system is designed to disconnect itself automatically at the first sign of critical fault conditions.
Rigorous Certification: Every product undergoes stringent testing (IEC62619, UN38.3, etc.) to ensure zero-defect safety.
Your Decision Checklist:
When choosing a home battery, prioritize brands that transparently offer these multi-layered safety designs. It’s your best guarantee of long-term, worry-free performance.
What to Do If a Lithium-ion Battery Explodes or Catches Fire
While unlikely, it’s crucial to know how to react.
- Evacuate and Call for Help: Your safety comes first. Get everyone away from the device and call the fire department immediately.
- Do Not Use Water (for large fires): Water can be ineffective on a large lithium battery fire and may conduct electricity. For small device fires (like a phone), a Class D fire extinguisher is best, but if unavailable, large amounts of water can be used to cool surrounding areas. For home energy storage fires, let the firefighters handle it—they are trained for this.
- Ventilate the Area: Battery fires can release toxic fumes. If safe to do so, open windows and doors on your way out.
How to Prevent Lithium Battery Explosions (Summary Tips)
While unlikely, it’s crucial to know how to react.
- Evacuate and Call for Help: Your safety comes first. Get everyone away from the device and call the fire department immediately.
- Do Not Use Water (for large fires): Water can be ineffective on a large lithium battery fire and may conduct electricity. For small device fires (like a phone), a Class D fire extinguisher is best, but if unavailable, large amounts of water can be used to cool surrounding areas. For home energy storage fires, let the firefighters handle it—they are trained for this.
- Ventilate the Area: Battery fires can release toxic fumes. If safe to do so, open windows and doors on your way out.
Lithium battery technology is the engine of our clean energy future. The minimal risks are effectively managed through superior engineering and informed use.
Polar ESS exists to deliver not just power, but confidence. We prove that through relentless focus on safety, you can harness the sun’s energy for your home without a second thought.
Choose wisely. Power safely. Live confidently — with Polar ESS.